3D Mapping Services
As one of the leading experts in the 3D Mapping Solutions, Devscout offers software solutions as well as consulting services, finding a high-quality, customized solution for every customer request.
What Is 3D Mapping Services?
3D mapping services involve the process of creating three-dimensional representations of objects, environments, or surfaces using specialized equipment and software. These services are often utilized in various industries such as architecture, urban planning, engineering, land surveys, and infrastructure inspections.
The primary goal of 3D mapping services is to accurately capture and visualize spatial data in three dimensions, allowing for enhanced understanding, analysis, and communication of geographical features, structures, or landscapes. This technology enables detailed modeling, simulation, and virtual exploration of real-world spaces, leading to improved decision-making, planning, and design processes.
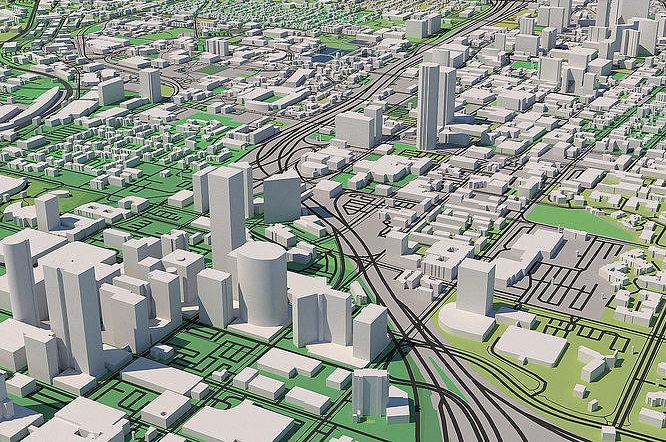
Some applications Devscout’s 3D Mapping Services can assist includes
Devscout, as a GIS development company, builds high-performing and precise 3D maps that are used in numerous progressive industries.
Real Estate
Today, 3D modeling for real estate has become a popular tool for designers, agents, and others working in the field. With the help of 3D mapping in real estate, we can visualize real estate objects as close to reality as possible. This aids in becoming familiar with all the nuances and making the right decisions during implementation.
Sustainable Energy
Helps identify optimal locations for wind, solar, or hydroelectric projects, maximizing energy production while minimizing environmental impact.
Allows real-time monitoring of energy infrastructure for optimal performance and timely maintenance, ensuring uninterrupted energy production.
Agriculture
3D mapping in precision agriculture involves using sensors and imaging technologies to create detailed three-dimensional maps of farms or fields, which help identify terrain variations, soil types, and crop health. Farmers can use this data to create customized prescription maps for precise application of inputs like fertilizers and pesticides, optimize irrigation, and address issues like soil erosion or drainage problems proactively.
Tourism
Immersive 3D maps offer a way to highlight your region’s attractions, heritage, and hidden gems. Elevate your online presence and engage potential tourists with a dynamic visual experience.
The 3D map can be visually and contextually customized to meet your local requirements, offering endless possibilities for personalization.
Transportation and Logistics
3D mapping software development services involve the creation and implementation of software solutions tailored to the needs of the transportation and logistics industry, utilizing 3D mapping technologies. These services aim to leverage 3D mapping to enhance various aspects of transportation and logistics operations, including route optimization, asset tracking and management, facility design and planning, last-mile delivery solutions, safety, and security.
Tools and Frameworks
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
3D Mapping Services We Offer
2D & 3D Digital Mapping Services
Devscout’s offer high-resolution 2D & 3D digital mapping services by converting geographic data into immersive and interactive high-resolution maps and visualizations.
Harnessing cutting-edge technologies like Cesium and Mapbox, we meticulously capture and process precise geographical data on regions, infrastructure, and structures. This data is then processed using advanced GIS software to produce high-resolution 2D and 3D maps and models. Our detailed visualizations are perfect for various applications, including urban planning, construction, environmental monitoring, and more.
3D Models and Visualizations
Utilizing cutting-edge technologies, we capture accurate data on buildings and infrastructure. This data is meticulously processed with advanced GIS software, resulting in the creation of 3D models and visualizations.
Our 3D models and visualizations are instrumental in a variety of applications, including facilities management, asset and facility management, plant 3D modeling, GIS for facilities management, training, and safety. These comprehensive tools support efficient and effective management, ensuring your facilities are maintained and operated at their best.
Web Map App Development
We specialize in designing custom mapping solutions for websites, applications, and data visualizations. Our maps are visually stunning and highly functional across all devices and browsers, ensuring a seamless user experience.
3D mapsproviding insightful data visualization, navigation support, and interactive features. With our expertise, your maps will not only look great but also deliver critical insights and drive user engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who uses 3D maps?
3D maps are finding applications in a wide range of industries and sectors, including: Urban planning and architecture, engineering and construction, real estate, gaming and entertainment, disaster management, environmental monitoring, navigation and tourism, education and research, cultural heritage preservation
As 3D mapping technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications emerge in the years to come.
What is the difference between 3D modeling and 3D mapping?
3D Modeling: Creates detailed, precise models of individual objects or characters using specialized software. Often used for animation, games, and product design.
3D Mapping: Captures existing environments or spaces, like buildings or landscapes, in 3D, often used for visualization of terrain, buildings, and landscapes.
What are the benefits of 3D mapping?
3D mapping offers a multitude of advantages, including:
Enhanced Visualization: 3D maps provide a more realistic and immersive representation of environments, allowing for better comprehension of spatial relationships, object dimensions, and overall layout.
Improved Planning: With a clear 3D visualization, stakeholders can make more informed decisions in various fields, such as urban planning, construction, engineering, and disaster management.
Better Navigation: 3D maps can enhance navigation systems, providing users with a better understanding of their surroundings, clearer directions, and more intuitive route planning.
Accurate Data Analysis: 3D maps can serve as a valuable data repository, enabling the collection, analysis, and visualization of spatial information for various applications.
Immersive Experiences and Storytelling: 3D maps can be used to create engaging and interactive experiences, such as virtual tours, historical reconstructions, and educational simulations.
Accessibility and Communication: 3D maps can make information more accessible to people with disabilities and can facilitate better communication and collaboration among diverse groups.
Emergency Response: Enhances situational awareness for emergency planning and response.
How to create a 3D map?
Creating a 3D map involves several steps, ranging from data acquisition to visualization:
Data Acquisition: Gather spatial data using satellite imagery, aerial photography, LiDAR, or other surveying methods.
Data Processing: Process the acquired data to generate a digital elevation model (DEM) or point cloud representing the terrain and features.
3D Modeling: Utilize 3D mapping software to create a 3D representation of the terrain, structures, or objects based on the processed data.
Texturing: Apply textures to the 3D models to enhance realism and visual appeal. This may involve incorporating satellite imagery, photographs, or other surface textures.
Integration: Integrate the 3D map with other systems or applications, such as GIS platforms or web mapping services, to provide interactive functionality and data sharing.
Visualization: Choose an appropriate visualization style, such as wireframe, shaded, or textured, to represent the 3D map effectively.
Testing and Refinement: Thoroughly test the 3D map for accuracy, usability, and performance. Refine the map based on testing results and user feedback.
What are the different types of 3D data in GIS?
In Geographic Information Systems (GIS), 3D data plays a crucial role in representing the real world with added depth and complexity. There are two main categories of 3D data used in GIS:
Feature Data: This type of data represents discrete objects in the real world with a 3D dimension. It uses geometry to define the object’s shape and location in space.
Surface Data: Surface data represents continuous features across an area, providing elevation information for the landscape. It allows for analysis and visualization of terrain, slopes, and other spatial relationships.
3D maps are finding applications in a wide range of industries and sectors, including: Urban planning and architecture, engineering and construction, real estate, gaming and entertainment, disaster management, environmental monitoring, navigation and tourism, education and research, cultural heritage preservation
As 3D mapping technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications emerge in the years to come.
3D Modeling: Creates detailed, precise models of individual objects or characters using specialized software. Often used for animation, games, and product design.
3D Mapping: Captures existing environments or spaces, like buildings or landscapes, in 3D, often used for visualization of terrain, buildings, and landscapes.
3D mapping offers a multitude of advantages, including:
Enhanced Visualization: 3D maps provide a more realistic and immersive representation of environments, allowing for better comprehension of spatial relationships, object dimensions, and overall layout.
Improved Planning: With a clear 3D visualization, stakeholders can make more informed decisions in various fields, such as urban planning, construction, engineering, and disaster management.
Better Navigation: 3D maps can enhance navigation systems, providing users with a better understanding of their surroundings, clearer directions, and more intuitive route planning.
Accurate Data Analysis: 3D maps can serve as a valuable data repository, enabling the collection, analysis, and visualization of spatial information for various applications.
Immersive Experiences and Storytelling: 3D maps can be used to create engaging and interactive experiences, such as virtual tours, historical reconstructions, and educational simulations.
Accessibility and Communication: 3D maps can make information more accessible to people with disabilities and can facilitate better communication and collaboration among diverse groups.
Emergency Response: Enhances situational awareness for emergency planning and response.
Creating a 3D map involves several steps, ranging from data acquisition to visualization:
Data Acquisition: Gather spatial data using satellite imagery, aerial photography, LiDAR, or other surveying methods.
Data Processing: Process the acquired data to generate a digital elevation model (DEM) or point cloud representing the terrain and features.
3D Modeling: Utilize 3D mapping software to create a 3D representation of the terrain, structures, or objects based on the processed data.
Texturing: Apply textures to the 3D models to enhance realism and visual appeal. This may involve incorporating satellite imagery, photographs, or other surface textures.
Integration: Integrate the 3D map with other systems or applications, such as GIS platforms or web mapping services, to provide interactive functionality and data sharing.
Visualization: Choose an appropriate visualization style, such as wireframe, shaded, or textured, to represent the 3D map effectively.
Testing and Refinement: Thoroughly test the 3D map for accuracy, usability, and performance. Refine the map based on testing results and user feedback.
In Geographic Information Systems (GIS), 3D data plays a crucial role in representing the real world with added depth and complexity. There are two main categories of 3D data used in GIS:
Feature Data: This type of data represents discrete objects in the real world with a 3D dimension. It uses geometry to define the object’s shape and location in space.
Surface Data: Surface data represents continuous features across an area, providing elevation information for the landscape. It allows for analysis and visualization of terrain, slopes, and other spatial relationships.
